Technical Details
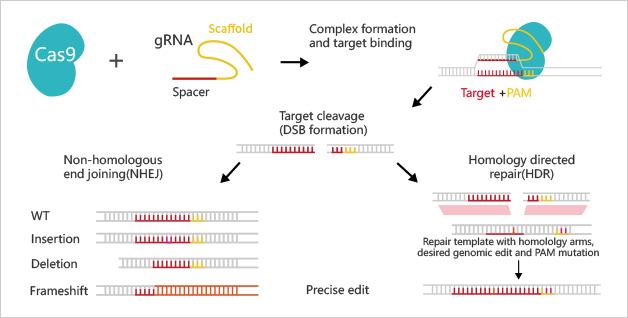
CRISPR/Cas9 system is a defense mechanism used by bacteria to resist the invasion of viruses and foreign plasmids. At present, the type II CRISPR/Cas9 system is the most developed and widely used system. It recognizes the target sequence with gRNA, and guide Cas9 endonuclease to cut the upstream of PAM, resulting in the double-strand break (DSB) of the target site DNA. To repair the DSB, the cell uses its own DNA repair mechanism to add or delete or replace pieces of DNA sequence via Homology Directed Repair (HDR) or Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ).
Close
CRISPR/Cas9 system is a defense mechanism used by bacteria to resist the invasion of viruses and foreign plasmids. At present, the type II CRISPR/Cas9 system is the most developed and widely used system. It recognizes the target sequence with gRNA, and guide Cas9 endonuclease to cut the upstream of PAM, resulting in the double-strand break (DSB) of the target site DNA. To repair the DSB, the cell uses its own DNA repair mechanism to add or delete or replace pieces of DNA sequence via Homology Directed Repair (HDR) or Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ).
Knockin Plasmid
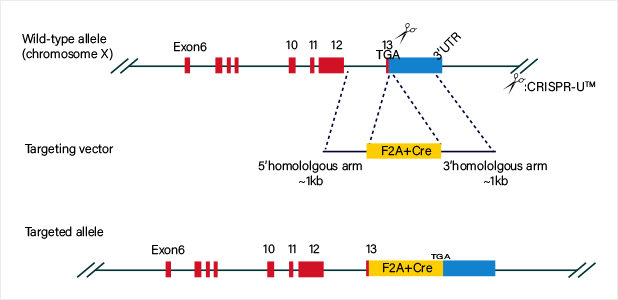
Knockin strategy
Guide RNA and Cas9 complex cause double-strand break (DSB) on the target site of DNA. Donor vector carrying knockin sequence is the template for homologous recombination repair (HDR), and it recombines to the target site.
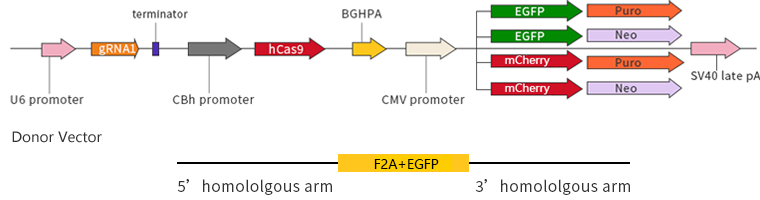
Knockin plasmid design
dual-gRNA/Cas9 all-in-one plasmid + Donor plasmid
Validation
Restriction enzyme digestion and sequencing
Application
Different species: mammals, zebrafish, primary cells, stem cells, cell lines, microorganisms, etc.
Different purposes: frame-shift mutation knockout, fragment knockout, precise knockout, point mutation, fragment knockin.